Smog Tech:
sensor-meaning
sensor-meaning
This is page 2 of sensor meaning from the previous page, for the Level 1 smog class or smog tech looking for information on passing the level 1 exam.
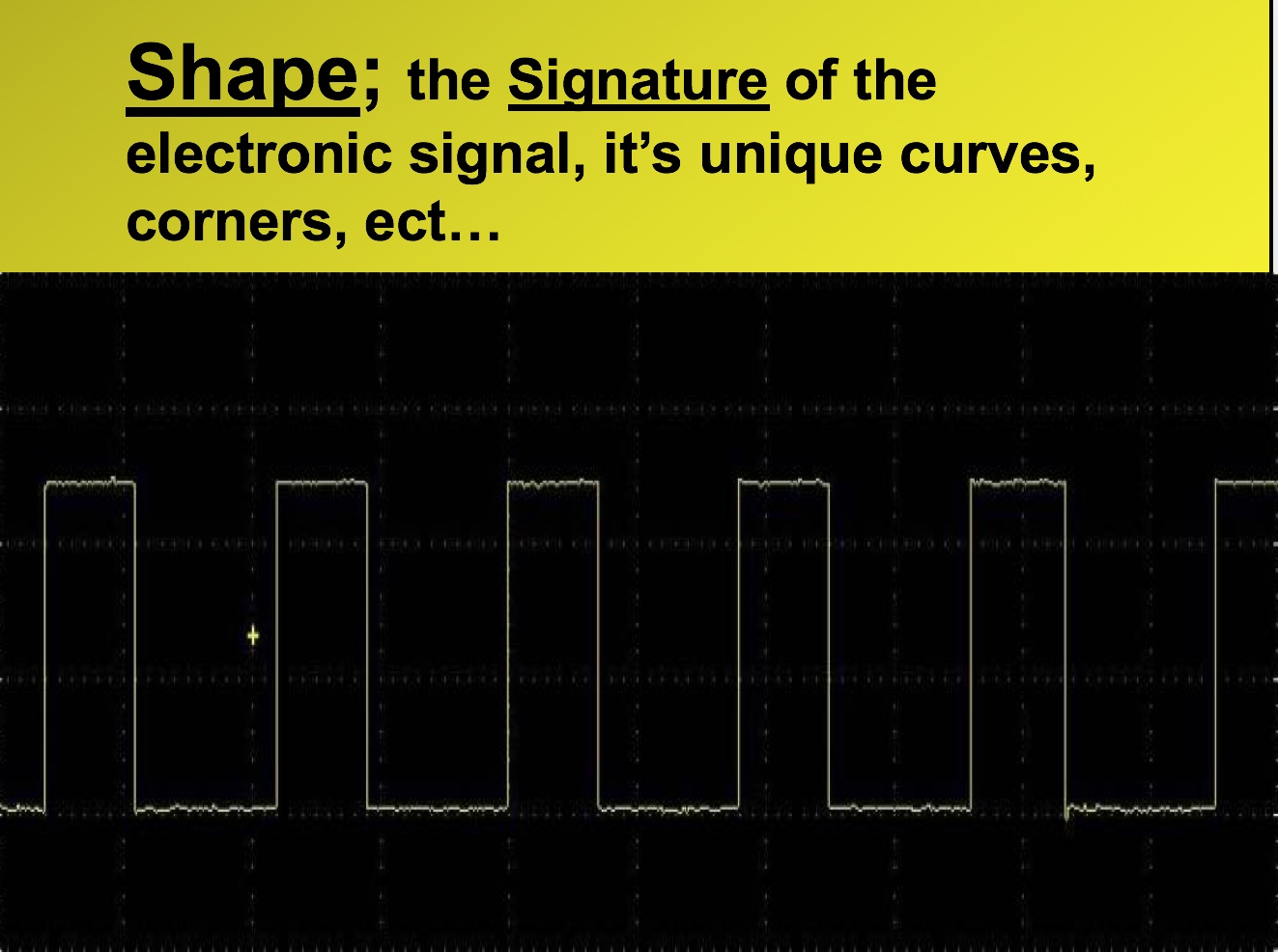
Before we go on to sensors, let’s understand digital signals, they can be input signals from a sensor or switch.
Digital signals can also be used to control output devices, for example, solenoids or stepper motors.
Digital signals are usually in the form of a square wave which is an on / off waveform.
Signal from Tech Help Update Class
Sensor-Meaning:
Thermistor
Most computer control vehicles use an engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
When the engine is cold, the vehicle needs to be richer this will help with cold starts prevent stalling and stumbling. The ECT notifies the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) when the car is cold with a voltage input to the PCM
When the engine warms up to operating temperature, the fuel mixture needs to be leaner for the best possible emissions. Again, the ECT provides this information into the PCM.
When the engine is cold, this sensor has the highest authority for starting cold and drivability, providing the crank and cam sensor is working correctly.
Most Engine Coolant Temperature Sensors are thermistors. Thermistors are usually a negative temperature coefficient thermistor (NTC).
What does this mean as the resistance decreases the temperature of the vehicle increases? The voltage input to PCM would be lower.
Also, as the vehicle temperature decreases the resistance increases, the voltage input to the PCM will be higher.
The Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IAT) is also an NTC sensor for the incoming air temperature.
All thermistors are not (ECT), engine coolant temperature sensors. A sensor that informs a body computer about temperature, such as an ambient air temperature for an AC system is known as a thermistor also.
Sensor-Meaning:
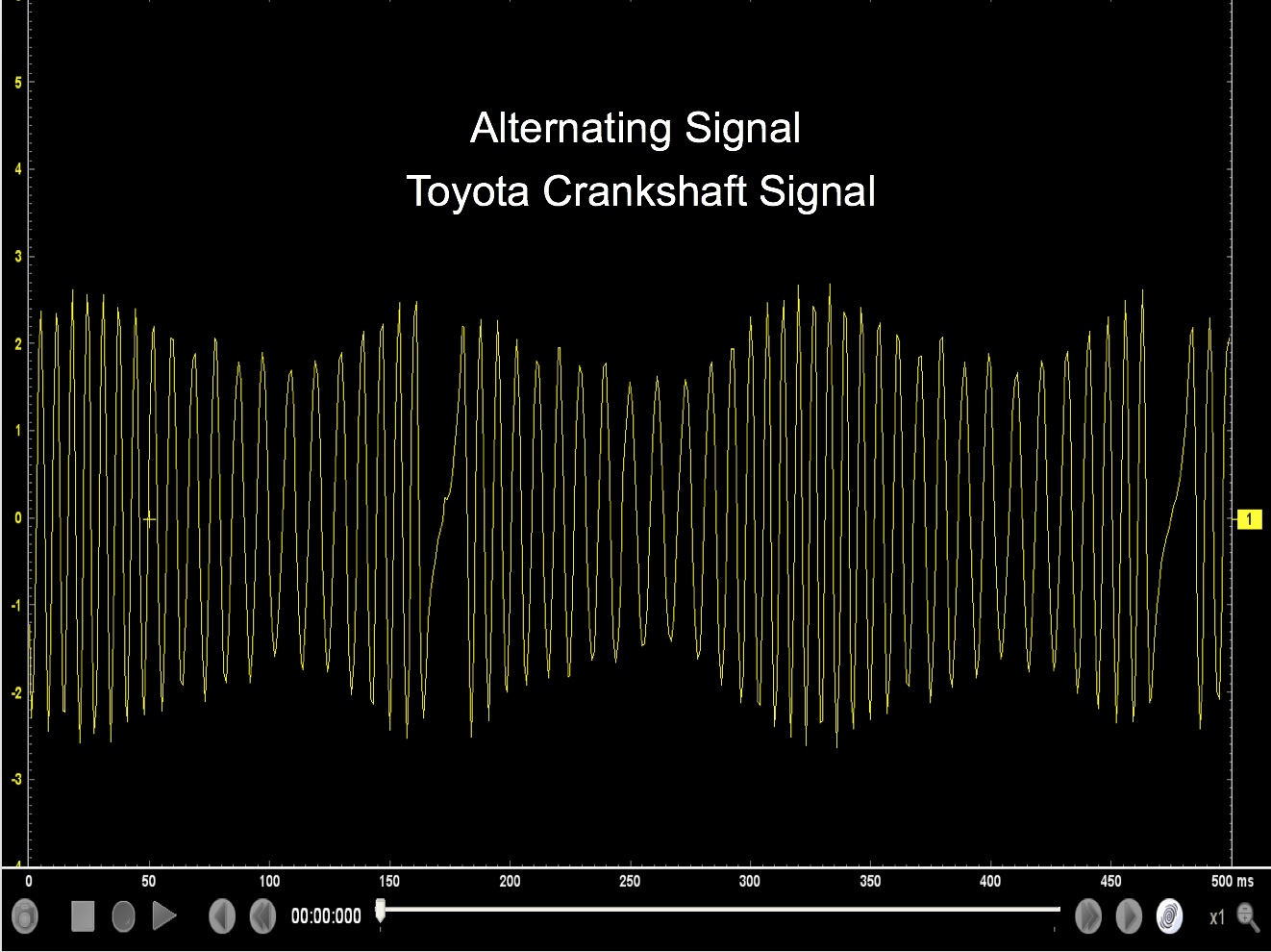
Permanent Magnetic Generator
A permanent magnetic generator sensor produces an alternating current (A/C) signal.
Sensors that produce an AC signal could be a crank or cam sensor, but the most common sensor is the vehicle wheel sensor.
Sensor Meaning
Close Loop and Open Loop
The oxygen sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust stream. There could be as has many four or more sensors on one car.
Open Loop is defined; when the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) ignores the O2 sensor. Anytime the PCM is not responding to O2 sensors it's called open loop.
The PCM will operate in a default mode, and that’s a slightly rich condition. The PCM will still process the information it receives from other sensors, but it will ignore the O2 sensor in Open Loop.
Closed Loop is basically when the PCM is responding to the O2 Sensors and balancing the air/fuel mixture. Close Loop operation in a fuel injection system is based on the oxygen content in the exhaust gases.
When the oxygen content is high, and the HO2S is producing a voltage lower than 450mv (lean condition) the PCM will respond with a rich command to the fuel injectors.
When the oxygen content is low, and the HO2S is producing a voltage higher than 451mv (rich condition) the PCM will respond with a lean command to the fuel injectors.
Most of the time the vehicle will operate in close loop; this is the best operating condition for the best emissions and fuel economy.
What does a vehicle need to go in to close loop?
1.) The vehicle needs to get to operating temperature
2.) The PCM timer needs to run out, usually 2 minutes
3.) The O2 sensor needs to be sending a reliable signal
Sensor-Meaning
Potentiometers
Most sensors have a two-wire connection with a 5-volt reference for power.
A Potentiometer is a three-wire connection with a 5- volt reference for power.
What is a potentiometer it’s a variable resistance sensor with a three-wire terminal with a 5-volt reference supply?
One end of the wire is the power supply, and the other end is the ground while the third wire or terminal is attached to a movable contact that slides across a resistor to vary the resistance.
Most potentiometers are on vane sensors, throttle position sensors and EGR position sensors.
MAP sensors are also three-wire sensors, but it's not a potentiometer, a Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor has a piezoresistive crystal.
The MAP sensor detects manifold pressure changes with changing throttle positions, which notifies the PCM if the vehicle is under a load.
Sensor-Meaning
Mass Air Flow Sensors
Most newer fuel injection vehicles use a Mass Air Flow Sensor some of the older fuel injection vehicles use the Vane Air Flow Sensor.
The Mass Air Flow or the Vane Sensor detects how much air is entering the engine once calculate the PCM can determine the load for proper fuel delivery.
Sensor-Meaning
Scan Tool PIDs
Most quality scan tools will give you Parameter Identification Data to read sensor data to make it easier to read. Also, a quality scan tool will provide you with actuator data and output control.
CLASS SCHEDULES
Emission Control 1:
B.A.R. Smog Check
Inspector Level 1
(Inspector "Smog" License):
Engine Fundamentals
8am - 12:15 pm
Summer Class
7/5/2022 -8/5/2022
Class # 799065
Emission Control 2:
B.A.R. Smog Check
Inspector Level 2
(Inspector "Smog" License):
Rules and Regulations
8am - 12:15 pm
Summer Classes
7/5/2022 - 8/5/2022
Class # 799067
Engine Performance 1:
8am - 12: 15 pm
Date: TBD
Class # 799069
Engine Performance 2:
B.A.R. Specified Diagnostic
and Repair Training
(Repair "Smog" License)
Time: TBD
Date: TBD
Class # 799071
Emission Control 1
(Inspector "Smog" License):
5:00pm - 8:45 pm
Date: TBD
Class # 799065
Emission Control 2:
(Inspector "Smog" License):
5:00pm - 8:45 pm
Date: TBD
Class # 799065
Exhaust Emissions (Update Class):
5:30 pm - 8:45 pm
Tuesday nights:
Dates: coming soon
Class # 796070